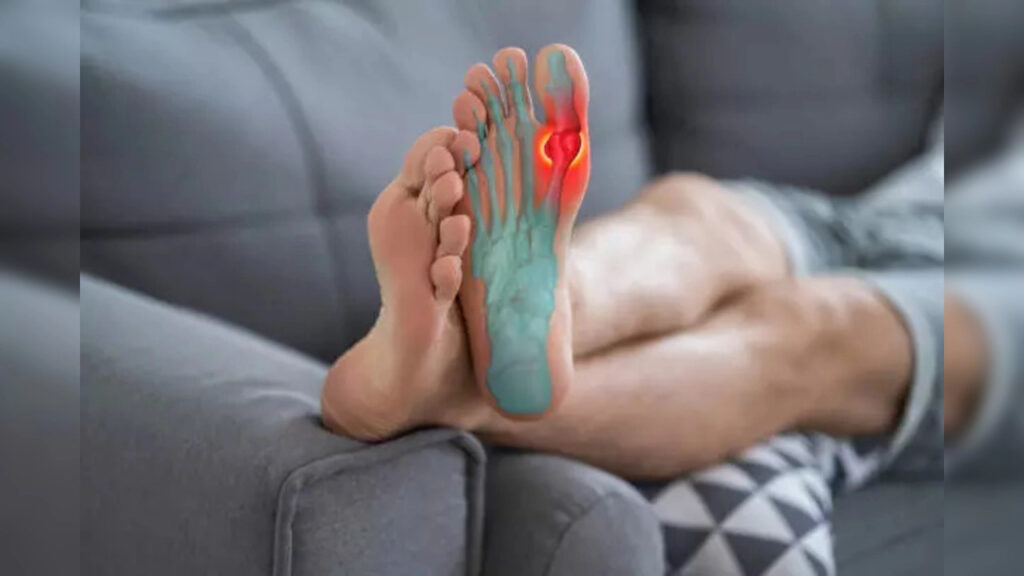
Do you experience persistent joint pain? This might indicate high uric acid levels in your blood. Understanding the link between joint pain and uric acid can help you manage and alleviate the discomfort effectively. Here’s a closer look at how uric acid affects your body and what you can do about it.
What is Uric Acid?
Uric acid is a waste product created when purines, which are compounds found in various foods, break down in the body. Purines are part of the process of digesting proteins and usually dissolve into the bloodstream. The kidneys then filter uric acid out of the blood and excrete it through urine. While uric acid itself serves no useful purpose, it can become problematic if levels rise too high.
When the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete it properly, uric acid crystals can form in the joints and tendons. These needle-like crystals can lead to intense inflammation, causing pain, swelling, and redness in the affected areas.
Uric Acid and Joint Pain
If uric acid accumulates in your body, it can lead to the formation of crystals in the joints and soft tissues. This buildup causes inflammation and discomfort, manifesting as arthritis-like symptoms. The pain associated with high uric acid levels often appears suddenly, particularly at night, and may be accompanied by symptoms such as fever and muscle aches. This condition is known as gout and can be extremely painful, with the first episode typically lasting from a few days to a few weeks and potentially affecting additional joints over time.
Understanding Gout
Gout is a specific type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It commonly affects the big toe but can occur in other joints as well. Gout attacks are marked by severe pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joint. Managing gout often involves making changes to your lifestyle and diet.
Symptoms of High Uric Acid
Common symptoms related to high uric acid levels include:
- Intense joint pain, often seen in gout.
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and muscle pain.
If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional may recommend a serum uric acid test to measure your uric acid levels. For reference, normal uric acid levels are generally 2.4-6.0 mg/dL for females and 3.4-7.0 mg/dL for males.
Managing Uric Acid Levels
To control uric acid levels and prevent joint pain, consider the following strategies:
- Diet: Incorporate more fiber into your diet and avoid sugary foods. A balanced diet can help regulate uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential. Adequate water intake helps to dilute uric acid in the blood and supports its elimination through urine.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can raise uric acid levels and hinder treatment. Reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption can be beneficial for managing uric acid levels.
Making these lifestyle changes can be an effective way to manage uric acid levels and alleviate joint pain. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can further reduce uric acid levels and lower the frequency of gout attacks.
Conclusion
Persistent joint pain could be a sign of high uric acid levels, which may lead to conditions like gout. By understanding the connection between uric acid and joint pain, and by making appropriate lifestyle changes, you can manage and reduce your symptoms. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle to ensure they align with your personal health needs.
Note: If you have any health-related concerns, please call us at +91-9058577992 for a free consultation with our experienced team. Thank you.